morton's neuroma compression test|latest treatment for morton's neuroma : exporters This test is also called Morton's test and it is used to check for a Morton's neuromain the intermetatarsal plantar digital nerve. See more CPF / CNPJ. Senha. Esqueci minha senha Entrar
{plog:ftitle_list}
28 de nov. de 2023 · The first expansion for Dune: Imperium , Rise of Ix expands and deepens the thrilling gameplay that has made Dune: Imperium one of the best board games of recent years. Acquire technology for .
This test is also called Morton's test and it is used to check for a Morton's neuromain the intermetatarsal plantar digital nerve. See more
The patient is positioned long sitting in a couch while the medial and lateral aspects of the forefoot of the patient are grasped by the clinician/examiner using one . See moreNeuromas generally result from the irritation of the intermetatarsal plantar digital nerve as it passes below the metatarsal ligament. Tight and poorly fitted footwears . See moreMulder's sign is a click heard during the test and it is thought to be produced by the gliding actions of the two metatarsals in the dorsal and plantar directions while . See more Ultrasound is particularly good at revealing soft tissue abnormalities, such as neuromas. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Using radio waves and a strong magnetic field, .
Interdigital Neuromas, also known as Morton's neuroma, is a compressive neuropathy of the interdigital nerve that often leads to plantar forefoot pain. Diagnosis is made clinically with tenderness over the plantar .A useful test for Morton's neuroma is the "lateral squeeze” or compression test: when the forefoot is compressed by the examiner’s hands a painful or palpable "Mulder's click" might be .

recovery after morton's neuroma surgery
Ultrasound (sonography) accurately demonstrates thickening of the interdigital nerve within the web space of greater than 3mm, diagnostic of a Morton’s neuroma. This typically occurs at the level of the intermetatarsal ligament. .Symptoms of Morton's neuroma may be replicated through the Gauthier' test, in which the forefoot is squeezed and medial to lateral pressure is applied . Bratkowski described a test that involves hyperextending the toes and rolling . Morton neuroma is a compressive neuropathy of the forefoot interdigital nerve. Neuropathy is mainly due to compression and irritation at the plantar aspect of the transverse intermetatarsal ligament. It is not a true neuroma as the condition is degenerative rather than neoplastic. It is also referred to as Morton metatarsalgia, interdigital neuritis, Morton .
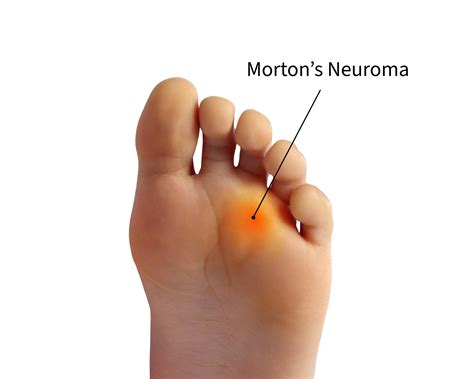
Morton's neuroma is a painful condition that affects the ball of your foot, most commonly the area between your third and fourth toes. Morton's neuroma may feel as if you are standing on a pebble in your shoe or on a fold . Find me here: https://linktr.ee/thephysiochannelFREE ONLINE COURSE (for therapists): Mastering Frozen Shoulder: https://daniel-lawrence-fc31.mykajabi.com/off.The exact cause of a Morton’s neuroma is not known, but current research suggests it is likely the result of entrapment (i.e., compression or squeezing) of the common digital plantar nerves. Compression of the nerve in the web space may trigger swelling and cause abnormal tissue to form in and around the nerve.Neural degeneration and perineural fibrosis are typical of Morton's neuroma[2]; the presence of inflammatory tissue in histological examination justifies the description of Morton's neuroma as perineural fibrosis.[3] Clinical symptoms that can help with diagnosis include pain and abnormal forefoot sensation. . space compression test .
Morton’s neuroma is a painful but benign growth of nerve tissue in the foot. If massage, exercise, and other remedies do not work, surgery is an effective option. . To test for Morton’s .
Metatarsal Squeeze Test (Morton’s Neuroma) The metatarsal squeeze test is used to detect a Morton’s or interdigital neuroma. To perform this test, support the patient’s foot in a relaxed position. Grasp the foot at the metatarsal heads and squeeze to compress them together. The test is positive if this produces pain, or if there is a .Morton’s neuroma can be confusing and very difficult to diagnose. . pain usually located between the third and fourth metatarsal heads which can frequently be reproduced by direct compression between the metatarsal heads. The disappearance of pain by local anesthesia into the painful metatarsal space (a diagnostic injection) is an important . Also called interdigital neuroma, Morton’s neuroma is a common cause of pain and/or paresthesias in the forefoot. Women are affected more than men, and age of onset is most often in the fifth or sixth decade. . Clinical tests for a Morton’s neuroma include the forefoot squeeze test, direct compression of the intermetatarsal space, and the .Various clinical maneuvers have been described to assist the clinician in the diagnosis of Morton's neuroma. The patient may demonstrate a Mulder's sign (), elicited by squeezing the forefoot and applying plantar and dorsal pressure.A positive test result consists of a click or pop that can be felt or heard; this can be painful to the patient.
www.mskmedicine.comA Morton’s neuroma is a common source of forefoot pain in patients who wear tight fitting shoes. Ultrasound evaluation is an inexpensive and easy way to diagnose a Morton’s neuroma. Diagnosis is aided with compression of the intermetarsal space with a .
Morton's neuroma is a condition that affects one of the nerves that run between the long bones (metatarsals) in the foot. . and swelling may then develop around a part of the nerve. This can look like a neuroma and can lead to compression of the nerve. The anatomy of the bones of the foot is also thought to contribute to the development of . Sensitivity & Accuracy . A Comparative Study 1 by Devendra Mahadevan to assess the diagnostic accuracy of 7 clinical tests for Morton’s neuroma (MN) compared with ultrasonography (US) on Forty patients (54 feet), he found that the Sensitivity & Accuracy of Mortons Neuroma Test was:. Sensitivity: 61%; Accuracy: 62%; Digital Nerve Stretch Test. .A compression test of the affected web space is quite specific . Morton neuroma is most likely a mechanically-induced degenerative neuropathy that predilects the third common digital nerve in middle-aged women who frequently wear fashionable shoes that are not designed for the physiology of the foot. A compression test of the affected web .Morton’s neuroma is caused by the entrapment and compression of the common digital plantar nerves, which often occur due to high impact activities such as running and jogging, sports that require tight fitting shoes, foot deformities, activities involving repetitive irritation to the ball of the foot, and wearing high heels or shoes with .
FIGURE 1 A rather large Morton's neuroma in a left third web space. placement of the Morton's neuroma from the two adjacent compressing metatarsal heads. Radiologically, a large Morton's neuroma can produce lateral toe deviation and can even occasionally cast a faintly ra diopaque shadow (Fig. 6). The size and shape of a
Morton's neuroma is a benign neuroma of an intermetatarsal plantar nerve, most commonly of the second and third intermetatarsal spaces (between the second/third and third/fourth metatarsal heads; the first is of the big toe), which results in the entrapment of the affected nerve.The main symptoms are pain and/or numbness, sometimes relieved by ceasing to wear footwear with . A neuroma—a.k.a. a nerve tumor or "pinched nerve"—is an often painful but typically benign abnormal growth of nerve tissue. Neuromas can occur anywhere in the body. A common type of neuroma in the foot, called Morton's neuroma, grows between the third and fourth toes. The hand is another common site for a neuroma to develop.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what is morton's neuroma also called?, where is plantar interdigital neuroma formed between?, who is plantar interdigital neuroma more common in? and more. . Test. Expert Solutions. Q-Chat. Live. Blast. Categories. . pathology of morton's neuroma may be external compression by . Can Morton's neuroma cause leg or calf pain? Morton's neuroma can indirectly lead to leg or calf pain. When a person experiences severe pain in the foot, it may alter their gait or walking pattern. This altered gait can cause leg or calf pain. What are the best shoes to wear for Morton's neuroma? Look for shoes with. A wide toe box to give the .
The most useful clinical test for the diagnosis of a Morton's neuroma is to perform a web space compression test which produces severe pain by squeezing the metatarsal heads together with one hand and simultaneously com- pressing the involved web space with the thumb and index finger of the opposite hand (Fig. 5). This compres- sion test can .
Morton’s neuroma, also called intermetatarsal neuroma, is the thickening of tissue in your toe. This tissue is next to a nerve. Pressure against the nerve irritates it and causes pain .
Causes of Morton's neuroma. Morton's neuroma is caused by an irritated or damaged nerve between the toe bones. It's often linked to: wearing tight, pointy or high-heeled shoes; doing a lot of running, or other sports or activities that place pressure on the feet; having other foot problems – such as flat feet, high arches, bunions or hammer toes Minimally invasive nerve decompression for operative management of Morton's neuroma has been shown to be an effective alternative to neurectomy; however, little is known about postoperative outcomes. In this retrospective case series, we reviewed 27 procedures in 25 patients who underwent minimally invasive nerve decompression as primary surgical .Section 3. Morton's intermetatarsal neuroma [Thomas, 2009a], and expert opinion in review articles [Coughlin, 2000; Adams, 2010; Di Caprio, 2018; Gougoulias, 2019; Bhatia, 2020; Puri, 2020]. Diagnosis of Morton's neuroma. The diagnosis of Morton’s neuroma is based on symptoms and clinical examination findings.Morton's neuroma is a common cause of forefoot pain. The exact cause of this nonneoplastic condition is not well known, although several theories have been proposed, including ischemia and mechanical compression of the plantar nerve against the transverse intermetatarsal ligament [].Histologic findings of Morton's neuroma include neural degeneration, epineural .
morton's neuroma surgery success rate
Meu MAIOR objetivo com esse canal é mostrar pra todos vocês que nossos sonhos podem se tornar realidade! VIVO POR VOCES, FAMILIA XERECRAZY 🤍.
morton's neuroma compression test|latest treatment for morton's neuroma